User-mode IPsec
2 minute read
This section outlines the setup and management of IPsec in user mode, including source files, build instructions, and execution steps.
Source
For user-mode IPsec, under mss/src/examples:
ipsec/linux/missiu/*ipsec_loadconfig/loadConfig_missiu.cipseckey_example_missiu.c
Build
To build IPsec user mode:
- Modify pre-defined compile flags in
make/Makefile.linux.ipsecas neededmake -f make/Makefile.linux.ipsec missiu
Note: Executables missiu, ike and loadConfig are generated under ./bin folder.
Run
To run IPsec user mode:
- Start
missiuto intercept packets in the data path:cd bin ./missiu -i <interface> [-l <log_file>] startRaw # packets are intercepted on the <interface> and the <log_file> is created in the /var/run/ folder. - New TAP device (e.g.,
tap0), is allocated, but may need to be brought up manually:ip link set dev tap0 up - Start IKE
./ike [-h] <local_ip_addr> & - Configure
./loadConfig -f <config_file> - Add a route to redirect outbound traffic to the TAP device.
- For example, if the
<config_file>contains:{ raddr 192.168.3.119 ulp icmp } ipsec { encr_algs aes encr_auth_algs sha1 } - Add a the following route:
route add -host 192.168.3.119 dev tap0
- For example, if the
Stop
To stop the process:
- Stop
ikeprocess:killall ike - Stop
missiufrom intercepting packets:./missiu -i <interface> stop
Additional information
In NanoSec, IKE to IPsec communications may be performed using the following:
- IOCTL (e.g. I/O Request Packet (IRP) to driver)
- PF_KEY (socket based)
- Direct APIs provided by IPsec
In the data path, packets may be processed as follows:
- User space service may use shared memory and IOCTL based events to receive/transit packets from a network driver (e.g. NDIS intermediate driver).
- User space process (in the forwarding plane) may call
IPSEC_applyfor outbound packets,IPSEC_permitfor inbound packets. In addition,IPSEC_fragRcv()reassembles fragmented packets.
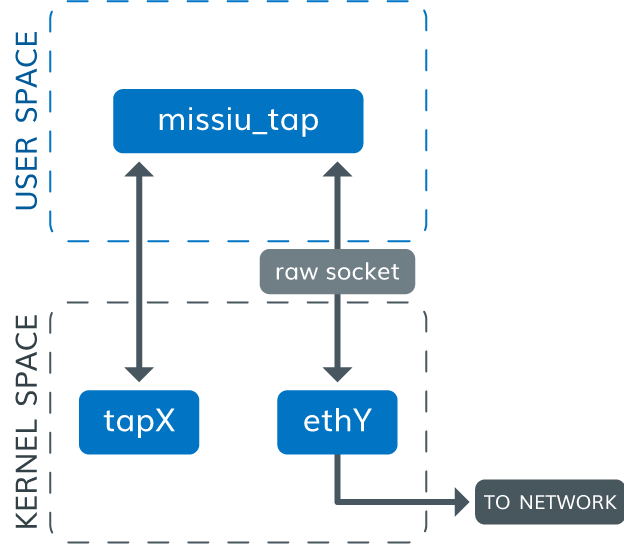
missiu TAP diagram
The following diagram shows the missiu TAP interactions between user space and kernel space.
missiu TAP interactions
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedback