NanoSSL client integration
7 minute read
Client integration process overview
This table describes the tasks for integrating NanoSSL client into an application.
| Task | Description | Refer to |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add the TrustCore SDK NanoSSL client software to the application development environment. | Building TrustCore SDK Components |
| 2 | If there is no pre-configured TrustCore SDK port for the operating system, edit the appropriate abstraction files to port the code to the operating system. | Porting TrustCore SDK Code |
| 3 | Specify which products (e.g., synchronous NanoSSL client), functions (e.g., debugging and examples), and features will be included in the TrustCore SDK executable by setting the appropriate compilation flags. For example, to incorporate synchronous and asynchronous NanoSSL clients into a system, define the following flags: | Building TrustCore SDK Components |
| NanoSSL compilation flags | ||
| 4 | Create the object files and executable. | Building TrustCore SDK Components |
| Using TrustCore SDK NanoCrypto FIPS Binaries for Linux | ||
| 5 | Add calls within the application’s code to the TrustCore SDK functions for initialization and shutdown, and then set up threads for any required TrustCore SDK components. | Common TrustCore SDK initialization |
| 6 | Add calls within the application’s code to the TrustCore SDK functions for NanoSSL client setup and message processing, and (optionally) certificate management. | Implement NanoSSL client |
| 7 | Optionally, if certificate management functions do not already exist within the application, add calls to the TrustCore SDK certificate management functions for performing certificate validation. | CERT_STORE_* functions, in the NanoSSL API Reference. |
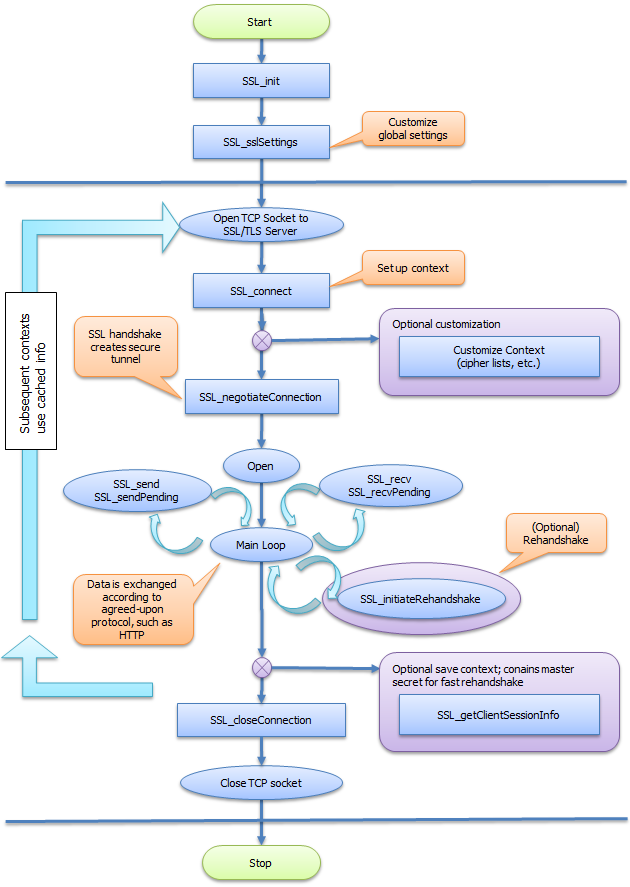
NanoSSL client process flow
This diagram shows the NanoSSL client process flow. For more information about the NanoSSL client process flow, see Implement NanoSSL client.
Build TrustCore SDK client sample code
To help with integration of NanoSSL client into devices, a suite of sample code is included in the source distribution (in the ${MSS_SRC_PKG}/src/examples directory), to quickly build a client and demonstrate its features using the provided NanoSSL cmake project and build scripts. The following files are provided:
ssl_client_example.c— Implements a secure, synchronous HTTP client.ssl_example_async_client.c— Implements a secure, asynchronous HTTP client.ssl_loopback_example.c— Implements an asynchronous client-server loop-back communication.
Sample code should be used as a reference and modified as required for inclusion into an application’s source code. The sample code may also be used to verify NanoSSL client-server communication.
Note
The moptions.h file does not need to be updated to generate this build; however, if using a makefile other than the one provided by DigiCert, the following flags need to be added:
__ENABLE_MOCANA_EXAMPLES____ENABLE_MOCANA_SSL_CLIENT
The following sections describe tasks that may be performed to generate and run sample NanoSSL Client code:
Generate a sample NanoSSL client
To generate the sample NanoSSL client:
- Change to the
projects/nanossldirectory:cd projects/nanossl - Run the following command:
./build.sh --clean --debug --suiteb ssl_client
Generate a TLS v1.3 sample NanoSSL client
To generate the TLS v1.3 sample NanoSSL client:
- Change to the
projects/nanossldirectory:cd projects/nanossl - Run the following command to build the NanoSSL library with support for TLS v1.3.
./build.sh --clean --debug --suiteb ssl_client
Disable TLS v1.3 and features
By default, TLS v1.3 is enabled when the NanoSSL client is generated.
To disable TLS v1.3 and features:
- Change to the
projects/nanossldirectory:cd projects/nanossl - Run the following command to build the NanoSSL library with TLS v1.3 features disabled:Where
./build.sh --clean --debug --suiteb ssl_client <disable-feature><disable-feature>may be:--disable-0rtt: Disables the 0-RTT feature.--disable-psk: Disables the PSK feature.--disable-tls13: Disables TLS v1.3.
Verify and run the sample NanoSSL client
If hosting an SSL server, we recommend verifying basic NanoSSL client communications with the SSL server before beginning implementations for custom code using the NanoSSL client sample code.
To verify and run the NanoSSL client sample code:
- Start the SSL server.
- Open a command shell and start the NanoSSL client.
- Run the sample NanoSSL client using the applicable command (i.e., using options for TLS or TLS v1.3) to securely connect via HTTPS to the SSL server, dump debug information to a temporary command prompt window, and then automatically terminate.
- For TLS:where
./bin/ssl_client <options><options>may be:?— Displays the help.-ssl_ip <IP>— Specifies the IP address of the SSL server.-ssl_port <ssl port>— Specifies the port number of the SSL server.-ssl_servername <ssl server name>— Specifies the SSL server’s name.-ssl_certpath <path to files>— Specifies the directory path to the certificate files.-ssl_server_cert <cert name>— Specifies the name of the server certificate.-ssl_client_cert <cert name>— Specifies the name of the client certificate.-ssl_client_keyblob <blob name>— Specifies the name of the client key BLOB file.
- For TLS v1.3:where additional
./bin/ssl_client <options><options>include:-ssl_external_psk— Specifies to use an external PSK for TLS v1.3.-ssl_early_data <early_data>— Specifies the early data content to be sent.
- For TLS:
Implement NanoSSL client
To integrate a NanoSSL client into an application, add calls to TrustCore SDK functions for NanoSSL client initialization, socket and connection management, message processing, and NanoSSL client shutdown, as shown in the ${MSS_SRC_PKG}/src/examples/ssl_client_example.c sample module.
In particular, the functions and tasks described in the table below should be performed in the order shown, making calls to either the synchronous or asynchronous methods as appropriate. For additional NanoSSL Client process flow information, see NanoSSL client process flow.
| Task | Synchronous reference | Asynchronous reference |
|---|---|---|
| Initialize NanoSSL client’s session manager and internal structures. | SSL_init | SSL_ASYNC_init |
| Set up certificates: create a certificate store, add identities and CA certificates to the store, and associate the certificate with the SSL connection. | CERT_STORE_* functions, in the NanoSSL API Reference. | CERT_STORE_* functions, in the NanoSSL API Reference. |
| Customize and register upcalls (callbacks) for all desired products and features. | Enabling NanoSSL and NanoDTLS products and features | |
| SSL_sslSettings | Enabling NanoSSL and NanoDTLS products and features | |
| SSL_sslSettings | ||
| Open a TCP socket connection to the NanoSSL server. | The application’s existing methods | The application’s existing methods. |
| Create a connection instance and establish session context. | SSL_connect | SSL_ASYNC_connect |
| Negotiate SSL handshaking. | SSL_negotiateConnection | SSL_ASYNC_start |
| Loop to continuously process packets. | SSL_send | |
| SSL_sendPending | ||
| SSL_recv | ||
| SSL_recvPending | SSL_ASYNC_sendMessage | |
| SSL_ASYNC_sendMessagePending | ||
| TCP read of data via SSL_ASYNC_recvMessage | ||
| SSL_ASYNC_recvMessage2 | ||
| SSL_ASYNC_getRecvBuffer | ||
| SSL_ASYNC_getSendBuffer | ||
| Invoke the asynchronous upcall to begin application communications | ||
| 7. a) Send flow | SSL_send: Sends application data to the connected client/server, then returns the number of bytes sent. | |
| SSL_sendPending: Gives the number of pending bytes. If SSL_send was not able to send all the bytes, SSL_sendPending should be called in a loop until all the data is sent | ||
| 7. b) Receive flow | SSL_recv: Reads application data from the connected client/server, then returns the total number of bytes received. | |
| SSL_recvPending: Indicates if there is any data to be read. SSL-recv should be invoked in a loop until SSL_recvPending indicates there is no data to be read. | ||
| Optionally, save the session context for later reconnection. | SSL_getClientSessionInfo | |
| SSL_getSessionFlags | SSL_getClientSessionInfo | |
| SSL_getSessionFlags | ||
| Reclaim device and NanoSSL client resources. | SSL_closeConnection | SSL_ASYNC_closeConnection |
| Close TCP socket connection to NanoSSL server. | The application’s existing methods | The application’s existing methods |
Optional NanoSSL client functions
This table lists optional functions that may also be performed:
| Optional function | Description |
|---|---|
SSL_enableCiphers | Limit which ciphers to use (for performance or security reasons). |
SSL_getCipherInfo | Retrieve the connection’s cipher and eccCurves. |
SSL_setDNSNames | Specify a list of DNS names that when matched to the certificate subject name will enable a connection. |
SSL_setServerNameList | Specify a list of server names acceptable to the client. |
SSL_getInstanceFromSocket | Retrieve the connection instance for a socket identifier. |
SSL_lookupAlert and SSL_sendAlert | Retrieve the SSL alert code for a TrustCore SDK error. |
SSL_getSocketId | Retrieve the socket identifier for a connection instance. |
SSL_ioctl (also see SSL_ioctl) | Dynamically enable and/or disable selected features for an SSL session’s connection instance. |
SSL_isSessionSSL | Determine whether a connection instance represents an SSL/TLS server, an SSL/TLS client, or an unrecognized connection (for example, SSH). |
SSL_initiateRehandshake | Renegotiate an SSL/TLSsession. |
SSL_setSessionFlags | Set session flags. |
SSL_getSessionStatus | Get session’s connection status. |
SSL_setVersionCallback | Log the TLS version during negotiation (using the __ENABLE_MOCANA_SSL_VERSION_LOG_CALLBACK__ compilation flag). |
SSL_setCookie and SSL_getCookie | Store and retrieve custom information for a connection instance’s context. |
SSL_releaseTables and SSL_shutdownStack | Shutdown sequence must be as follows: |
SSL_setCipherAlgorithm | Set ciphers, supported groups, signature algorithms, and certificate signature algorithms to be used during TLS v1.3 negotiation. |
SSL_sendKeyUpdateRequest | Invoke the flow to update the keys used to encrypt/decrypt application data. |
SSL_setClientSavePSKCallback | Set a callback to save PSK sent by server. |
SSL_CLIENT_setRetrievePSKCallback | Send a callback to retrieve the PSK to use to establish a new connection. |
SSL_setEarlyData | Set application data to be sent as early data in the 0-RTT flow. |
SSL_serializePSK | Serialize PSK data. |
SSL_deserializePSK | De-serialize PSK data. |
SSL_setMinRSAKeySize | Set the minimum size of the RSA key used in the connection. |
SSL_setSha1SigAlg | Enable/disable the SHA-1 signature algorithm. |
SSL_setFIPSEnabled | Enable/disable FIPS. |
SSL_setClientCAList | Set the list of accepted CAs on the server. This CA list is sent in the Certificate Request message. |
SSL_populateMutualAuthCertStore | Populate the certificate store for mutual authentication per session. |
SSL_enableSrtpProfiles | Set the SRTP profiles to be used by the DTLS SRTP feature. |
SSL_enableHeartbeatSupport | Enable heartbeat support for the connection. |
SSL_sendHeartbeatMessage | Send the heartbeat message. |