Customize a NanoSSH server implementation
9 minute read
After building and verifying the NanoSSH server example code, the NanoSSH server implementation may be customized and integrated into an application.
Before customizing the example code or using it as a model for another implementation, first verify that it builds and executes as expected in the intended environment; see Building NanoSSH server example code.
NanoSSH server build flags
Customize your build by using these NanoSSH server build flags and CMake options. All flags are optional.
Tip
For a complete list of build flags, see API Reference.Standard Edition
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
__DISABLE_OPEN_SSH_AES_GCM__ | Excludes AES-GCM cipher support from the OpenSSH implementation. |
__DISABLE_MOCANA_INIT__ | Skips Mocana-specific global initialization during library startup. |
__DISABLE_MOCANA_SSH_COMMON_NAME_CHECK__ | Turns off Common Name (CN) validation in SSH X.509 certificate authentication. |
__DISABLE_MOCANA_SSH_RSA_KEY_EXCHANGE__ | Removes RSA key-exchange algorithms from the SSH handshake. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_DSA__ | Builds DSA cryptographic primitives in the Mocana crypto layer. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_ASYNC_SERVER_API__ | Compiles the asynchronous SSH server API (non-blocking event loop). |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_CHANNEL_ID_DEBUG__ | Adds verbose logging of SSH channel IDs for troubleshooting. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_X509V3_SIGN_SUPPORT__ | Enables X.509 v3 certificate signing operations in SSH. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_DSA_SUPPORT__ | Allows DSA host and user keys in SSH sessions (auth + sign). |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_FTP_SERVER__ | Includes the SFTP/SCP file-transfer server components. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_MAX_SESSION_TIME_LIMIT__ | Enforces a compile-time maximum session duration timer. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_OLD_DSA_CONVERSION__ | Converts legacy DSA key blobs to the current format at load time. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_PING__ | Adds keep-alive “ping” messages to detect dead SSH connections. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_PORT_FORWARDING__ | Compiles local, remote, and dynamic port-forwarding support. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_RSA_SUPPORT__ | Allows RSA host and user keys in SSH sessions. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_SCP_SERVER__ | Builds the SCP (secure copy) server handler. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_SENDER_RECV__ | Separates sender and receiver threads for higher throughput. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_SERVER__ | Compiles the full SSH server library. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_STREAM_API__ | Exposes a stream-oriented (stdio-like) SSH API layer. |
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_X509V3_RFC_6187_SUPPORT__ | Adds RFC 6187 X.509-based SSH authentication. |
__ENABLE_SSH_VERSION1_SUPPORT__ | Re-enables deprecated SSH-1 protocol compatibility. |
__USE_MOCANA_SSH_SERVER__ | Forces linkage against the Mocana SSH server instead of OpenSSH. |
Community Edition
| Scenario | CMake flags | Server command | Client command |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public‑key authentication | -DBUILD_SAMPLES=ON | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -port 8818 | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_client -ip 127.0.0.1 -port 8818 -username admin -password secure |
| Disable SSH server library | -DDISABLE_SSH_SERVER | – | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_client -ip 127.0.0.1 -port 8818 -username admin -password secure |
| Disable SSH client library | -DDISABLE_SSH_CLIENT | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -port 8818 | – |
| Server certificate authentication | -DENABLE_SSH_SERVER_CERT_AUTH=ON | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -ssh_server_cert $SSH_SERVER_CERT -ssh_server_blob $SSH_SERVER_KEYBLOB | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_client -ssh_ca_cert $SSH_SERVER_CA_CERT |
| Client certificate authentication | -DENABLE_SSH_CLIENT_CERT_AUTH=ON | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -ssh_ca_cert $SSH_CLIENT_CA_CERT | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_client -ssh_client_cert $SSH_CLIENT_CERT -ssh_client_blob $SSH_CLIENT_KEYBLOB |
| Mutual certificate authentication | -DENABLE_SSH_SERVER_CERT_AUTH=ON -DENABLE_SSH_CLIENT_CERT_AUTH=ON | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -ssh_server_cert $SSH_SERVER_CERT -ssh_server_blob $SSH_SERVER_KEYBLOB -ssh_ca_cert $SSH_CLIENT_CA_CERT | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bins/ssh_client -ssh_client_cert $SSH_CLIENT_CERT -ssh_client_blob $SSH_CLIENT_KEYBLOB -ssh_ca_cert $SSH_SERVER_CA_CERT |
| Shell example (client shell) | -DENABLE_SSH_CLIENT_SHELL_EXAMPLE=ON | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -port 8818 | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_client -ip 127.0.0.1 -port 8818 -username admin -password secure |
| Asynchronous API example | -DENABLE_SSH_ASYNC_API_SUPPORT=ON | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_server -port 8818 | export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=lib/:crypto_lib/linux-x86_64/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH./samples/bin/ssh_client -ip 127.0.0.1 -port 8818 -username admin -password secure |
| Secure path restriction | -DSECURE_PATH="/path/to/directory" | – | – |
Asynchronous NanoSSH server process
To integrate an asynchronous NanoSSH server into an application, add calls to the application for NanoSSH server initialization, socket and connection management, message processing, and NanoSSH server shutdown, as shown in the src/examples/ssh_example.c example module.
In particular, the functions and tasks described below should be performed in the order shown.
- Add the NanoSSH server Software
- Incorporate the NanoSSH server software into the application development environment, ensuring the inclusion of example code that aligns closely with the intended application.
- Port TrustCore SDK Code
- If no pre-configured TrustCore SDK port exists for the operating system, modify the appropriate abstraction files to adapt the code to the operating system.
- Specify Features for TrustCore SDK Executable
- Determine which features, such as debugging and examples, should be included in the TrustCore SDK executable by setting the appropriate compilation flags. Initially, only a minimal set of flags should be defined to limit functionality to basic communications. After constructing a basic example application and verifying its executability in the environment (refer to step 5), repeat this step to incrementally add more features.
- Create Object Files and Executable
- Proceed with the creation of object files and the executable.
- Verify NanoSSH server example code
- Confirm that the NanoSSH server example code operates correctly on the operating system.
- Iterative Feature Addition
- Reiterate steps 3 to 5 as necessary to incrementally introduce additional features.
Note
See NanoSSH server compilation flags above for compilation flag options and details.Asynchronous NanoSSH server common functions
The following NanoSSH server functions are used to communicate both synchronously and asynchronously with SSH clients, and are therefore applicable to the asynchronous NanoSSH server:
- Connection management functions:
- SSH_getCookie
- SSH_setCookie
- SSH_releaseTables
- SSH_shutdown
- SSH_assignCertificateStore
- Security functions:
- SSH_convertOldKeyBlobToNew
- SSH_compareAuthKeys
- SSH_getInstanceFromSocket
- SSH_getNextConnectionInstance
- SSH_getSessionCryptoInfo
- SSH_getSocketId
- SSH_verifyPublicKeyFile
- SSH_setUserPortForwardingPermissions
- SSH_useThisCipherList
- SSH_useThisHmacList
- SSH_initiateReKey
- SSH_numBytesTransmitted
- SSH server management functions:
- SSH_getTerminalSettingDescr
- SSH_sshSettings
- SSH_ioctl
- Port Forwarding functions:
- SSH_setUserPortForwardingPermissions
- SSH_sendPortForwardMessage
- SSH_sendPortForwardClose
- SSH_ackPortFwdReceivedMessageBytes
Asynchronous functions for NanoSSH server
The following functions are used to communicate asynchronously with SSH clients:
- Connection management functions:
- SSH_ASYNC_init
- SSH_ASYNC_acceptConnection
- SSH_ASYNC_closeConnection
- SSH_ASYNC_startProtocolV2
- Messaging functions:
- SSH_ASYNC_recvMessage
- SSH_ASYNC_ackReceivedMessageBytes
- SSH_ASYNC_recvContinueMessage
- SSH_ASYNC_sendMessage
- SSH_ASYNC_sendMessagePending
Callback functions for asynchronous NanoSSH server
NanoSSH server callback functions should be customized for an application. Registering callbacks entails assigning custom functions to the session callback function pointers (the functions that begin with funcPtr) of the sshSettings structure.
- General purpose callbacks:
- funcPtrPasswordAuth
- funcPtrPubKeyAuth
- funcPtrKeyIntAuthReq
- funcPtrReleaseKeyIntReq
- funcPtrGetAuthAdvertizedMethods
- funcPtrConnect
- funcPtrConnection
- funcPtrPostAccept
- funcPtrStartTimer
- Protocol-specific callbacks:
- funcPtrSessionOpen
- funcPtrPtyRequest
- funcPtrOpenShell
- funcPtrOpenSftp
- funcPtrWindowChange
- funcPtrReceivedData
- funcPtrStdErr
- funcPtrEof
- funcPtrClosed
- funcPtrBreakOp
- Port forwarding callback functions:
- funcPtrConnect
- funcPortFwdReceivedData
- funcPortFwdPtrClosed
- funcPortFwdPtrEof
Customize a synchronous NanoSSH server implementation
After building and verifying NanoSSH server example code, the synchronous NanoSSH server implementation may be customized and integrated into an application.
Before customizing the example code or using it as a model for another implementation, first verify that it builds and executes as expected in the intended environment; see Building NanoSSH server Example Code.
Synchronous NanoSSH server process
To integrate a synchronous NanoSSH server into an application, add calls to the application for NanoSSH server initialization, socket and connection management, message processing, and NanoSSH server shutdown, as shown in the src/examples/ssh_example.c example module.
In particular, the functions and tasks described in Table 4 should be performed in the order shown. For additional synchronous NanoSSH server process flow information, see Figure 2.
- Define Flags
- Define any necessary flags for the implementation by editing the
moptions.hfile.
- Define any necessary flags for the implementation by editing the
- Generate Keys (Optional)
- Optionally generate public and private keys to store in the device’s persistent storage.
- Initialize NanoSSH server
- Initialize the NanoSSH server’s session manager, internal structures, and specific settings.
- Configure Callbacks
- Configure common (synchronous and asynchronous) callbacks:
- Replace stub functions with any custom routines, modeling them after the NanoSSH example code.
- Register the required callbacks (functions marked with an asterisk are automatically registered for synchronous use).
- Configure common (synchronous and asynchronous) callbacks:
- Configure Synchronous Callbacks
- Configure synchronous callbacks as needed.
- Accept TCP Socket Connection
- Accept a TCP socket connection from the NanoSSH server using the application’s existing methods.
- Establish SSH Session
- Establish an SSH session between the device and a web browser.
- Negotiate NanoSSH Handshaking
- Conduct the negotiation for NanoSSH handshaking.
- Process Packets
- Continuously loop to process packets.
- Reclaim Resources
- Reclaim device and NanoSSH server resources.
- Shut Down NanoSSH Stack (Optional)
- Optionally shut down the NanoSSH stack if no longer needed.
- Build NanoSSH-Integrated Implementation
- Build the NanoSSH-integrated implementation.
Note
See NanoSSH server compilation flags above for compilation flag options and details.Synchronous NanoSSH server flowchart
Below shows the NanoSSH synchronous server process flowchart. For additional information about the NanoSSH synchronous server process flow, see above.
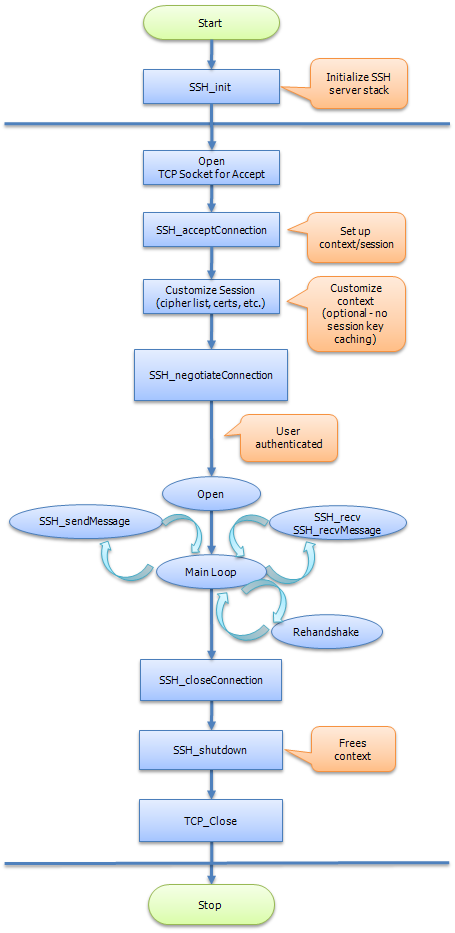
Common Functions for Synchronous NanoSSH server
The following NanoSSH server functions are used to communicate both synchronously and asynchronously with SSH clients (whether NanoSSH Client or a third-party SSH client), and are therefore applicable to synchronous NanoSSH server implementations:
- Connection management functions:
- SSH_getCookie
- SSH_setCookie
- SSH_releaseTables
- SSH_shutdown
- SSH_assignCertificateStore
- Security functions:
- SSH_convertOldKeyBlobToNew
- SSH_compareAuthKeys
- SSH_getInstanceFromSocket
- SSH_getNextConnectionInstance
- SSH_getSessionCryptoInfo
- SSH_getSocketId
- SSH_verifyPublicKeyFile
- SSH_setUserPortForwardingPermissions
- SSH_useThisCipherList
- SSH_useThisHmacList
- SSH_initiateReKey
- SSH_numBytesTransmitted
- SSH server management functions:
- SSH_getTerminalSettingDescr
- SSH_sshSettings
- SSH_ioctl
- Port forwarding functions:
- SSH_setUserPortForwardingPermissions
- SSH_sendPortForwardMessage
- SSH_sendPortForwardClose
- SSH_ackPortFwdReceivedMessageBytes
Synchronous functions for NanoSSH server
The following functions are used to communicate synchronously with SSH clients (whether NanoSSH Client or a third-party SSH client):
- Connection management functions:
- SSH_acceptConnection
- SSH_closeConnection
- SSH_init
- SSH_negotiateConnection
- SSH_sendPing
- Messaging functions:
- SSH_recv
- SSH_recvMessage
- SSH_recvPending
- SSH_sendMessage
- SSH_sendErrMessage
- SSH server management functions:
- SSH_disconnectAllClients
- SSH_startserver
- SSH_stopserver
Callback functions for synchronous NanoSSH server
NanoSSH server callback functions should be customized for an application. Registering callbacks entails assigning custom functions to the session callback function pointers (the functions that begin with funcPtr) of the sshSettings structure.
- General purpose callbacks:
- funcPtrPasswordAuth
- funcPtrPubKeyAuth
- funcPtrKeyIntAuthReq
- funcPtrReleaseKeyIntReq
- funcPtrGetAuth Advertized Methods
- funcPtrConnect
- funcPtrConnection
- funcPtrPostAccept
- funcPtrStartTimer
- Protocol-specific callbacks:
- funcPtrSessionOpen
- funcPtrPtyRequest
- funcPtrOpenShell
- funcPtrOpenSftp
- funcPtrWindowChange
- funcPtrReceivedData
- funcPtrStdErr
- funcPtrEof
- funcPtrClosed
- funcPtrBreakOp
- funcPtrExec
- funcPtrReplyPing
- Port forwarding callback functions:
- funcPtrConnect
- funcPortFwdReceivedData
- funcPortFwdPtrClosed
- funcPortFwdPtrEof
Customize a NanoSSH SFTP server implementation
The NanoSSH SFTP server enables secure file transfers. In addition, it may protect individual files and directories on systems for which there is no such mechanism, such as many embedded operating systems. If desired, subdirectories and files may inherit the closest progenitor’s (parent’s) file permissions. Files may be mapped to disk, RAM, Flash, remote storage, and more.
The figure below shows how a server’s virtual file system, SFTP:/, may differ from the actual file system; in this case, the NVRAM:/root directory of a Flash-based file system. The client sees four top-level directories (log, scripts, root_ca, and firmware), a subdirectory (ui, under firmware), and another subdirectory (bin, under ui). Each of these directories is mapped to a directory in the actual NVRAM file system, effectively hiding the remaining NVRAM files and directories.
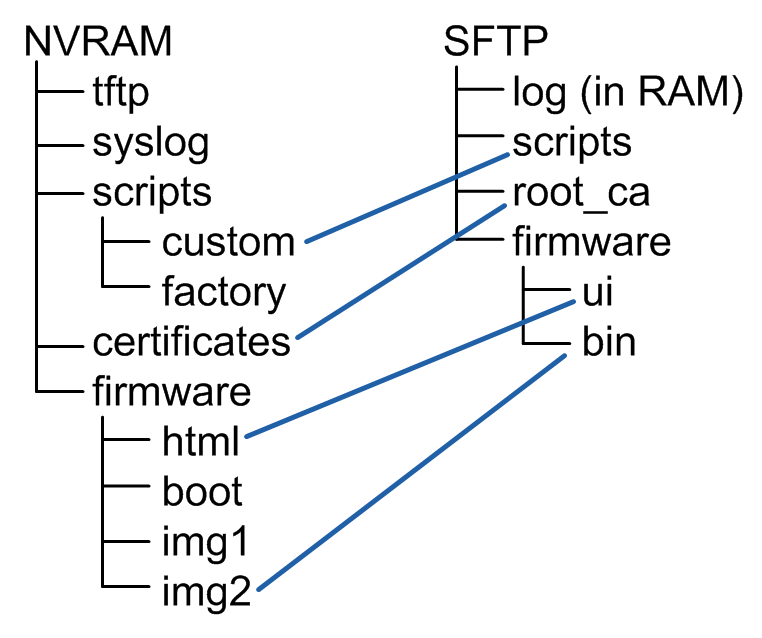
NanoSSH SFTP server process overview
NanoSSH SFTP server integration entails adding compilation flags and replacing the stub functions for file I/O with custom routines, as shown in the src/examples/sftp_example.c example module.
In particular, the tasks described below should be performed in the order shown.
- Define Implementation Flags
- Define any necessary flags for the implementation by editing the
moptions.hfile.
- Define any necessary flags for the implementation by editing the
- Enable SFTP server
- Enable the SFTP server functionality within the NanoSSH server by setting the
__ENABLE_MOCANA_SSH_FTP_SERVER__flag.
- Enable the SFTP server functionality within the NanoSSH server by setting the
- Write File System Routines
- Develop file system routines tailored for the target embedded systems.
- Replace Stub Functions
- Replace stub functions with any custom routines tailored for your system.
- Set Up Virtual Filesystem and Permissions
- Set up the virtual filesystem and directory permissions by adding entries to the
sftpFiles[]table. - See the implementation example in
sftp_example_filesys.cin the examples directory.
- Set up the virtual filesystem and directory permissions by adding entries to the
- Rebuild NanoSSH-Integrated Implementation
- Rebuild the NanoSSH-integrated implementation to incorporate all changes and new configurations.
Compilation flags and predefined values for NanoSSH SFTP server
The compilation flags for the NanoSSH SFTP server focus on enabling specific features and functionalities critical for the secure file transfer capabilities of the server.
Functions for NanoSSH SFTP server
The following functions may be used in NanoSSH SFTP server implementations:
- server management settings:
- SSH_sftpSettings
- Security context initialization functions:
- SSH_sftpSetMemberOfGroups
- SSH_sftpSetHomeDirectory
- Context state management functions (embed the context within the NanoSSH SFTP context):
- SSH_sftpSetCookie
- SSH_sftpGetCookie
- File transfer functions:
- SSH_sftpReadLocation
- SSH_sftpReadBuffer
- SSH_sftpReadBufferSize
- SSH_sftpNumBytesRead
- SSH_sftpWriteLocation
- SSH_sftpWriteBuffer
- SSH_sftpWriteBufferSize
Callback functions for NanoSSH SFTP server
NanoSSH SFTP callback functions should be customized for an application. To register callbacks, assign any custom functions to the following session callback function pointers (the functions that begin with funcPtr) of the sftpSettings structure:
- File I/O callback functions:
- funcPtrOpenFileUpcall
- funcPtrReadFileUpcall
- funcPtrWriteFileUpcall
- funcPtrCloseFileUpcall
- Directory management and traversal callback functions:
- funcPtrCreateDir
- funcPtrRemoveDir
- funcPtrOpenDirUpcall
- funcPtrReadDirUpcall
- funcPtrCloseDirUpcall
- File management callback functions:
- funcPtrGetFileStats
- funcPtrGetOpenFileStats
- funcPtrRemoveFile
- funcPtrRenameFile